PHP에서 파일의 마지막 줄을 읽는 가장 좋은 방법은 무엇입니까?
내 PHP 응용 프로그램 에서 많은 파일 (대부분 로그) 의 끝에서 시작하여 여러 줄 을 읽어야합니다 . 때로는 마지막 하나만 필요하고 때로는 수십 또는 수백이 필요합니다. 기본적으로 저는 Unix tail명령 만큼 유연한 것을 원합니다 .
파일에서 마지막 줄 하나를 얻는 방법에 대한 질문이 있습니다 (하지만 N 줄이 필요 합니다), 다른 솔루션이 제공되었습니다. 어느 것이 최고이고 어느 것이 더 나은지 잘 모르겠습니다.
방법 개요
인터넷에서 검색하면서 다양한 솔루션을 발견했습니다. 세 가지 접근 방식으로 그룹화 할 수 있습니다.
file()PHP 기능 을 사용하는 순진한 것 ;tail시스템에서 명령 을 실행하는 속임수 ;- 강력한 행복하게 사용하여 열린 파일을 움직이지 있다는 것
fseek().
나는 결국 다섯 가지 해결책, 순진한 하나, 속임수 하나 및 세 가지 강력한 솔루션을 선택 (또는 작성) 했습니다.
- 내장 배열 함수를 사용 하는 가장 간결하고 순진한 솔루션 입니다.
- 약간 큰 문제가있는 command 기반
tail의 유일한 솔루션 :tail사용할 수없는 경우 (Unix가 아닌 Windows) 또는 시스템 기능을 허용하지 않는 제한된 환경에서는 실행되지 않습니다. - 개행 문자를 검색하고 계산하는 파일 끝에서 단일 바이트 를 읽는 솔루션은 여기 에서 찾을 수 있습니다 .
- 멀티 바이트 버퍼 큰 파일 최적 솔루션을 발견 여기 .
- 버퍼 길이가 동적 인 솔루션 # 4 의 약간 수정 된 버전으로 , 검색 할 라인 수에 따라 결정됩니다.
모든 솔루션이 작동 합니다. 어떤 파일에서든 그리고 우리가 요청하는 라인의 수에 대해 예상 된 결과를 반환한다는 의미에서 (대용량 파일의 경우 PHP 메모리 제한을 깨고 아무것도 반환하지 않을 수있는 솔루션 # 1 제외). 그러나 어느 것이 더 낫습니까?
성능 테스트
질문에 답하기 위해 테스트를 실행합니다. 그게 이런 일이 이루어지는 방법입니다.
내 디렉토리에 있는 여러 파일을 결합 하는 샘플 100KB 파일을 준비했습니다 /var/log. 그런 다음 다섯 가지 솔루션 중 하나를 사용 하여 파일 끝에서 1, 2, .., 10, 20, ... 100, 200, ..., 1000 줄 을 검색하는 PHP 스크립트를 작성했습니다 . 각 단일 테스트는 10 번 반복되며 (예 : 5 × 28 × 10 = 1400 테스트) 평균 경과 시간 을 마이크로 초 단위로 측정 합니다.
PHP 명령 줄 인터프리터를 사용하여 로컬 개발 컴퓨터 (Xubuntu 12.04, PHP 5.3.10, 2.70GHz 듀얼 코어 CPU, 2GB RAM)에서 스크립트를 실행합니다. 결과는 다음과 같습니다.
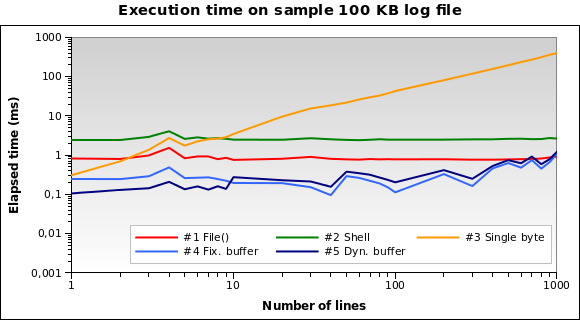
솔루션 # 1과 # 2가 더 나쁜 것 같습니다. 솔루션 # 3은 몇 줄을 읽어야 할 때만 좋습니다. 솔루션 # 4 및 # 5가 최고의 솔루션 인 것 같습니다. 동적 버퍼 크기가 알고리즘을 최적화 할 수있는 방법에 유의하십시오. 버퍼 감소로 인해 실행 시간이 몇 줄에 대해 조금 더 짧습니다.
더 큰 파일로 시도해 봅시다. 10MB 로그 파일 을 읽어야한다면 어떨까요?
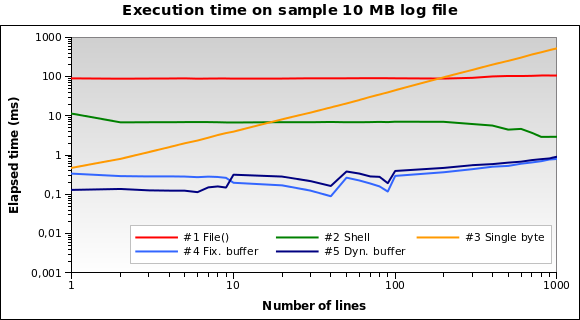
이제 솔루션 # 1은 훨씬 더 나쁜 것입니다. 사실 전체 10MB 파일을 메모리에로드하는 것은 좋은 생각이 아닙니다. 1MB와 100MB 파일에서도 테스트를 실행했는데 거의 같은 상황입니다.
그리고 작은 로그 파일의 경우? 이것은 10KB 파일에 대한 그래프입니다 .
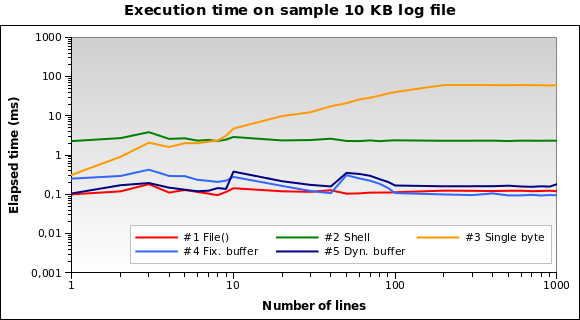
솔루션 # 1이 지금 최고의 솔루션입니다! 10KB를 메모리에로드하는 것은 PHP에서 큰 문제가 아닙니다. 또한 # 4와 # 5가 잘 수행됩니다. 그러나 이것은 가장 중요한 경우입니다. 10KB 로그는 150/200 라인과 같은 것을 의미합니다.
여기 에서 모든 테스트 파일, 소스 및 결과를 다운로드 할 수 있습니다 .
마지막 생각들
솔루션 # 5 는 일반적인 사용 사례에 적극 권장됩니다. 모든 파일 크기에서 잘 작동하며 몇 줄을 읽을 때 특히 잘 수행됩니다.
10KB보다 큰 파일을 읽어야하는 경우 솔루션 # 1을 피하십시오 .
솔루션 # 2 와 # 3 은 내가 실행하는 각 테스트에 가장 적합한 솔루션 이 아닙니다. # 2는 2ms 미만으로 실행되지 않으며 # 3은 요청한 줄 수에 크게 영향을받습니다 (1 줄 또는 2 줄에서만 작동합니다. ).
이것은 마지막 줄을 건너 뛸 수도있는 수정 된 버전입니다.
/**
* Modified version of http://www.geekality.net/2011/05/28/php-tail-tackling-large-files/ and of https://gist.github.com/lorenzos/1711e81a9162320fde20
* @author Kinga the Witch (Trans-dating.com), Torleif Berger, Lorenzo Stanco
* @link http://stackoverflow.com/a/15025877/995958
* @license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
*/
function tailWithSkip($filepath, $lines = 1, $skip = 0, $adaptive = true)
{
// Open file
$f = @fopen($filepath, "rb");
if (@flock($f, LOCK_SH) === false) return false;
if ($f === false) return false;
if (!$adaptive) $buffer = 4096;
else {
// Sets buffer size, according to the number of lines to retrieve.
// This gives a performance boost when reading a few lines from the file.
$max=max($lines, $skip);
$buffer = ($max < 2 ? 64 : ($max < 10 ? 512 : 4096));
}
// Jump to last character
fseek($f, -1, SEEK_END);
// Read it and adjust line number if necessary
// (Otherwise the result would be wrong if file doesn't end with a blank line)
if (fread($f, 1) == "\n") {
if ($skip > 0) { $skip++; $lines--; }
} else {
$lines--;
}
// Start reading
$output = '';
$chunk = '';
// While we would like more
while (ftell($f) > 0 && $lines >= 0) {
// Figure out how far back we should jump
$seek = min(ftell($f), $buffer);
// Do the jump (backwards, relative to where we are)
fseek($f, -$seek, SEEK_CUR);
// Read a chunk
$chunk = fread($f, $seek);
// Calculate chunk parameters
$count = substr_count($chunk, "\n");
$strlen = mb_strlen($chunk, '8bit');
// Move the file pointer
fseek($f, -$strlen, SEEK_CUR);
if ($skip > 0) { // There are some lines to skip
if ($skip > $count) { $skip -= $count; $chunk=''; } // Chunk contains less new line symbols than
else {
$pos = 0;
while ($skip > 0) {
if ($pos > 0) $offset = $pos - $strlen - 1; // Calculate the offset - NEGATIVE position of last new line symbol
else $offset=0; // First search (without offset)
$pos = strrpos($chunk, "\n", $offset); // Search for last (including offset) new line symbol
if ($pos !== false) $skip--; // Found new line symbol - skip the line
else break; // "else break;" - Protection against infinite loop (just in case)
}
$chunk=substr($chunk, 0, $pos); // Truncated chunk
$count=substr_count($chunk, "\n"); // Count new line symbols in truncated chunk
}
}
if (strlen($chunk) > 0) {
// Add chunk to the output
$output = $chunk . $output;
// Decrease our line counter
$lines -= $count;
}
}
// While we have too many lines
// (Because of buffer size we might have read too many)
while ($lines++ < 0) {
// Find first newline and remove all text before that
$output = substr($output, strpos($output, "\n") + 1);
}
// Close file and return
@flock($f, LOCK_UN);
fclose($f);
return trim($output);
}
이것은 또한 작동합니다.
$file = new SplFileObject("/path/to/file");
$file->seek(PHP_INT_MAX); // cheap trick to seek to EoF
$total_lines = $file->key(); // last line number
// output the last twenty lines
$reader = new LimitIterator($file, $total_lines - 20);
foreach ($reader as $line) {
echo $line; // includes newlines
}
또는없이 LimitIterator:
$file = new SplFileObject($filepath);
$file->seek(PHP_INT_MAX);
$total_lines = $file->key();
$file->seek($total_lines - 20);
while (!$file->eof()) {
echo $file->current();
$file->next();
}
불행히도 귀하의 테스트 케이스는 내 컴퓨터에 segfault가 있으므로 어떻게 수행되는지 알 수 없습니다.
여기에서이 모든 것을 읽은 후 내 작은 복사 붙여 넣기 솔루션. tail ()은 $ fp를 닫지 않으므로 어쨌든 Ctrl-C로 종료해야합니다. usleep은 CPU 시간을 절약하기 위해 지금까지 Windows에서만 테스트되었습니다. 이 코드를 클래스에 넣어야합니다!
/**
* @param $pathname
*/
private function tail($pathname)
{
$realpath = realpath($pathname);
$fp = fopen($realpath, 'r', FALSE);
$lastline = '';
fseek($fp, $this->tailonce($pathname, 1, false), SEEK_END);
do {
$line = fread($fp, 1000);
if ($line == $lastline) {
usleep(50);
} else {
$lastline = $line;
echo $lastline;
}
} while ($fp);
}
/**
* @param $pathname
* @param $lines
* @param bool $echo
* @return int
*/
private function tailonce($pathname, $lines, $echo = true)
{
$realpath = realpath($pathname);
$fp = fopen($realpath, 'r', FALSE);
$flines = 0;
$a = -1;
while ($flines <= $lines) {
fseek($fp, $a--, SEEK_END);
$char = fread($fp, 1);
if ($char == "\n") $flines++;
}
$out = fread($fp, 1000000);
fclose($fp);
if ($echo) echo $out;
return $a+2;
}
또 다른 기능으로 정규식을 사용하여 항목을 구분할 수 있습니다. 용법
$last_rows_array = file_get_tail('logfile.log', 100, array(
'regex' => true, // use regex
'separator' => '#\n{2,}#', // separator: at least two newlines
'typical_item_size' => 200, // line length
));
함수:
// public domain
function file_get_tail( $file, $requested_num = 100, $args = array() ){
// default arg values
$regex = true;
$separator = null;
$typical_item_size = 100; // estimated size
$more_size_mul = 1.01; // +1%
$max_more_size = 4000;
extract( $args );
if( $separator === null ) $separator = $regex ? '#\n+#' : "\n";
if( is_string( $file )) $f = fopen( $file, 'rb');
else if( is_resource( $file ) && in_array( get_resource_type( $file ), array('file', 'stream'), true ))
$f = $file;
else throw new \Exception( __METHOD__.': file must be either filename or a file or stream resource');
// get file size
fseek( $f, 0, SEEK_END );
$fsize = ftell( $f );
$fpos = $fsize;
$bytes_read = 0;
$all_items = array(); // array of array
$all_item_num = 0;
$remaining_num = $requested_num;
$last_junk = '';
while( true ){
// calc size and position of next chunk to read
$size = $remaining_num * $typical_item_size - strlen( $last_junk );
// reading a bit more can't hurt
$size += (int)min( $size * $more_size_mul, $max_more_size );
if( $size < 1 ) $size = 1;
// set and fix read position
$fpos = $fpos - $size;
if( $fpos < 0 ){
$size -= -$fpos;
$fpos = 0;
}
// read chunk + add junk from prev iteration
fseek( $f, $fpos, SEEK_SET );
$chunk = fread( $f, $size );
if( strlen( $chunk ) !== $size ) throw new \Exception( __METHOD__.": read error?");
$bytes_read += strlen( $chunk );
$chunk .= $last_junk;
// chunk -> items, with at least one element
$items = $regex ? preg_split( $separator, $chunk ) : explode( $separator, $chunk );
// first item is probably cut in half, use it in next iteration ("junk") instead
// also skip very first '' item
if( $fpos > 0 || $items[0] === ''){
$last_junk = $items[0];
unset( $items[0] );
} // … else noop, because this is the last iteration
// ignore last empty item. end( empty [] ) === false
if( end( $items ) === '') array_pop( $items );
// if we got items, push them
$num = count( $items );
if( $num > 0 ){
$remaining_num -= $num;
// if we read too much, use only needed items
if( $remaining_num < 0 ) $items = array_slice( $items, - $remaining_num );
// don't fix $remaining_num, we will exit anyway
$all_items[] = array_reverse( $items );
$all_item_num += $num;
}
// are we ready?
if( $fpos === 0 || $remaining_num <= 0 ) break;
// calculate a better estimate
if( $all_item_num > 0 ) $typical_item_size = (int)max( 1, round( $bytes_read / $all_item_num ));
}
fclose( $f );
//tr( $all_items );
return call_user_func_array('array_merge', $all_items );
}
나는 다음 방법을 좋아하지만 최대 2GB의 파일에서는 작동하지 않습니다.
<?php
function lastLines($file, $lines) {
$size = filesize($file);
$fd=fopen($file, 'r+');
$pos = $size;
$n=0;
while ( $n < $lines+1 && $pos > 0) {
fseek($fd, $pos);
$a = fread($fd, 1);
if ($a === "\n") {
++$n;
};
$pos--;
}
$ret = array();
for ($i=0; $i<$lines; $i++) {
array_push($ret, fgets($fd));
}
return $ret;
}
print_r(lastLines('hola.php', 4));
?>
'UFO ET IT' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Microsoft.Office.Interop Visual Studio를 찾을 수 없습니다. (0) | 2020.11.16 |
|---|---|
| 테스트를 통해 pytest 클래스를 올바르게 설정하고 분해하는 방법은 무엇입니까? (0) | 2020.11.16 |
| PHP 재귀 함수를 사용하여 디렉토리의 모든 파일 및 폴더 나열 (0) | 2020.11.15 |
| 캔버스를 마우스 커서로 확대 (0) | 2020.11.15 |
| 사용자 정의 Sublime Text 2 스 니펫의 범위 정의 (0) | 2020.11.15 |